Part 1
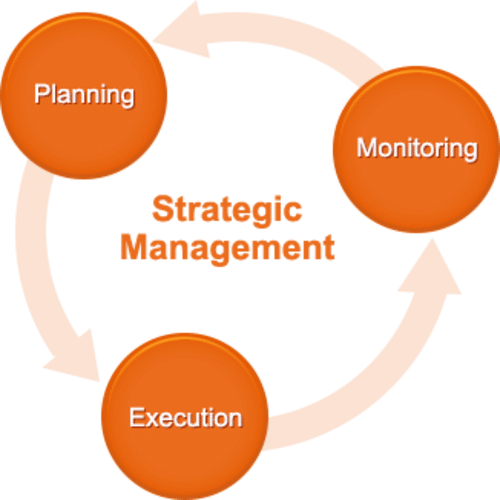
Strategic management refers to understanding the strategic position of an organization. The process of strategic management involves the methods to explore corporate strategies of organizations. Strategic management helps the organizations to examine the activities of top executives (Ketchen & Short, 2012). The concept of strategic management used in the organizations these days has borrowed various ideas from the strategic management of ancient times. In the classical military, all the major decisions were considered as strategic while the minor decisions were considered as tactical. In 1491 BC, a hierarchical delegation of authorities by Moses is the best. . .















